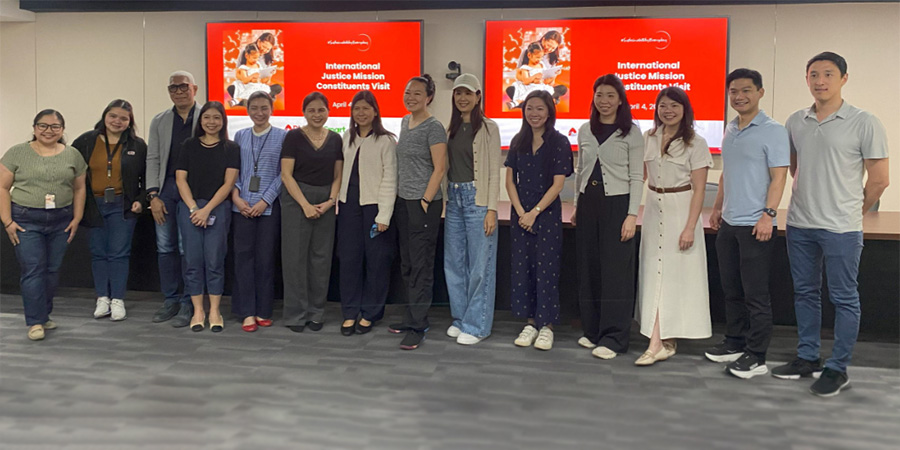
PLDT Inc. (PLDT) and its wireless unit, Smart Communications, Inc. (Smart), are working together with the anti-trafficking organization, International Justice Mission (IJM) Philippines, to help the Philippine government address the increasing cases of online sexual abuse and exploitation of children (OSAEC) in the country.
During a recent public hearing of the Senate Committee on Women, Children, Family Relations, and Gender Equality, it was highlighted that OSAEC accounted for a significant portion of the 17,600 cases of child rights violations in 2023, as reported by the Philippine National Police (PNP) Women and Children Protection Center.
Latest: MobiFone Seeks Approval to Serve National Defense and Security
Senator Risa Hontiveros also referenced IJM’s study, which revealed that almost half a million Filipino children were trafficked online through live streaming in 2022, involving foreign offenders working with local perpetrators for financial gain. PLDT, Smart, and IJM have been collaborating with law enforcement agencies, child protection advocates, and philanthropists from different countries to address the issue of OSAEC in the Philippines and promote cooperation to protect Filipino children online.
In September 2024, PLDT and Smart supported IJM in organizing a national summit that involved President Ferdinand Marcos, Jr., the Department of Justice Inter-Agency Council Against Trafficking, the Department of Interior and Local Government, PNP units, and leaders from various organizations to prioritize child protection at a national level. President Marcos, Jr. instructed all government agencies and local units to intensify efforts to combat OSAEC and incorporate child safety into all initiatives and regulations.
PLDT and Smart have also been engaging with IJM constituents from the United States of America, Hong Kong, and South Korea to raise awareness about industry solutions and garner international support for local efforts against OSAEC.
Interesting Read: Money Goes Mobile: Asia Embraces Digital Transactions
Melissa Vergel de Dios, Chief Sustainability Officer of PLDT and Smart, emphasized, “While rapidly evolving technologies such as AI bring new capabilities beneficial to everyday life, these are also being used to enable OSAEC, making such crimes against children even more difficult to address. Recognizing this, we at PLDT and Smart continue to update our multi-pronged approach to combat OSAEC. This includes complementing our child protection platform with key partnerships like that with IJM to further strengthen our response and support to the Philippine government’s whole-of-society approach against OSAEC.”
Samson Inocencio Jr., National Director of IJM Philippines, added, “The Philippines is setting a global precedent in building a strong, multi-sectoral response to the scourge of online sexual exploitation of children. Tackling this complex crime requires strategic partnerships across both public and private sectors. PLDT and Smart’s commendable collaboration with the Philippine government and child protection advocates is helping pave the way for a safer world for children. IJM remains committed to working with PLDT and Smart to continually refine and strengthen solutions that protect children both online and offline.”
In addition to their work with IJM, PLDT and Smart are cooperating with the National Telecommunications Commission, law enforcement agencies, and courts to investigate and prosecute OSAEC cases. The telcos received and fulfilled 46 lawful requests for information related to OSAEC cases in 2024.
Furthermore, PLDT and Smart have blocked over 1.7 million URLs and online content associated with OSAEC from June 2021 to February 2025, as part of their commitment to human rights and child safeguarding policies in compliance with Republic Act 11930, also known as the Anti-OSAEC and Anti-Child Abuse and Exploitation Materials Law.
Latest Reads:
Aussie Broadband, Optus Extend Mobile Partnership
Satellites vs. Subsea: Navigating Asia’s Future of Connectivity
Malaysia’s Mobile Service Revenue to Hit USD 6.1 Billion by 2029